Content available at: Español (Spanish)

- What kind of data should a publication provide us with?
- What do the different results obtained in the studies tell us?
- How should we interpret them?
A scientific article should, in addition to informing us of a series of findings made by the authors, be a guide that allows other researchers, following the same (or similar) methods and materials reach (or not) similar conclusions. than the authors thereof.
What should we look for when reading an article?
Bradbury et al. in table 3 of their article, reported the effect of phytase levels between days 1 to 14, using a 2 x 2 x 2 factorial design (two sources of calcium, two levels of calcium and two levels of phytase, see table 1).
The mean is a descriptive statistical parameter of a population.
There are multiple descriptive statistical parameters such as mean, standard deviation, proportion, etc.
At the beginning of the experiment, the authors or ourselves did not know the real data of the weight gain, the consumption and the conversion index of the total chicken population (Cobb-500 in this case).
From the 1120 chickens used in this experiment, we collect the samples, and estimate the value of the statistical parameter of interest, in this case the mean.
Would we always get the same results when testing a sample of 1120 Cobb-500 chickens? Of course not, they can be very similar, but not the same, that is why the value we obtain from a sample is called the estimate of the mean and as such has an associated error.
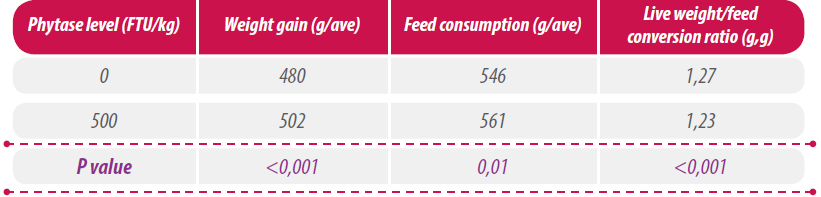
Table 1: Influence of dietary treatment on the productive results of chickens during the period of 1 to 14 days of life (modified from Bradbury et al. 2017).
The value of the statistic (the mean) of the sample is used to estimate the value of the unknown parameter of the population. If the samples are random, the statistics give unbiased point estimates of the corresponding parameters.
However, as a result, the point estimate does not give us enough information about the test.
Keep up to date with our newsletters
Receive the magazine for free in digital version REGISTRATION ACCESS
YOUR ACCOUNT LOGIN Lost your password?

