Content available at: Español (Spanish)
Campylobacter is one of the top four global causes of diarrhea-related illnesses and is considered the most common bacterial cause of gastroenteritis in the world. Campylobacteriosis is considered to be a zoonosis, meaning it is a disease that can be transmitted to humans directly by animals or indirectly via by-products of animal origin.
Food accounts for 80% of zoonosis transmissions.
- Chicken meat accounts for 60-70%. The bird’s body temperature is very suitable for C. jejuni, 41 ° C-42 ° C, without developing pathology.
- 20% raw milk, and some cheeses, comes from C. fetus infection of the udder.
- Water, including recreational waters. As a vector of faecal contamination, an outbreak was identified in the USA in the 1980s from mains water that affected around 3,000 people.
- Vegetables, irrigation with water from farms close to the crop gardens.
- Farm animals, pig as a vector for C. coli and companion animals.
- Farm and slaughterhouse staff, veterinarians. Operators with an enteric condition are highly contagious.
Given the scope of the problem, somehow it should be contemplated in the legislation with a note on this microorganism.
- One of the fundamental objectives of food law is to ensure a high level of protection of public health. The microbiological risks of food products are one of the main sources of foodborne illness for people. Food products must not contain microorganisms or their toxins or metabolites in amounts that pose an unacceptable risk to human health.
Regulation (EC) n ° 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of January 28, 2002, establishes the general principles and requirements of food law.
- The Committee highlights Salmonella, Campylobacter, verotoxigenic E.coli and Listeria monocytogenes as priorities. It establishes the obligations of food companies to make zoonosis and / or zoonotic agents subject to surveillance and keep the results and isolated strains at the disposal of the authority.
Directive 2003/99 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of November 17, 2003, on the surveillance of zoonoses and zoonotic agents.
- Apply the principles of the hazard analysis and critical points control (HACCP) system established in the Codex Alimentarius.
Regulation (EC) No. 852/2004, relating to the hygiene of food products.
- Said updated regulation introduces a pending proposal as of today, which establishes:
Commission Regulation (EC) No. 2073/2005 of November 15, 2005.
Two countries specifically have tried to reduce the presence of the bacterium by implementing biosecurity measures, Great Britain and the Netherlands. The results have not been satisfactory and the cost of production of the birds has increased.
TAXONOMY
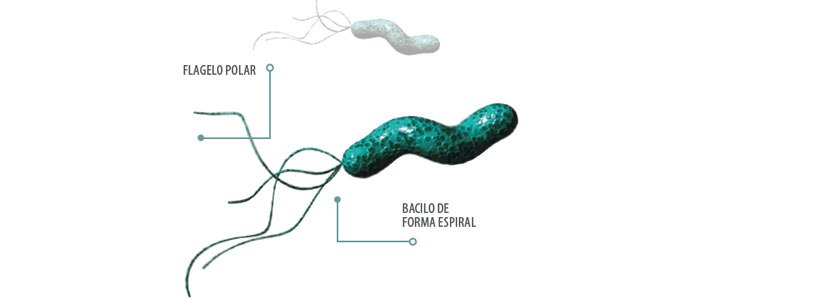
Family Campylobacteriaceae, Genus Campylobacter, with 17 species and 8 subspecies. Spiral-shaped Bacillus, curved, Gram negative, it has a polar flagellum in one or both poles that gives it mobility, facilitating intestinal invasion. Involved in pathology due to the production of endotoxins, cytotoxins.
Today there are commercial and highly efficient means and solutions available to create microaerophilic conditions, making it easy to analyze and detect Campylobacter spp.. Some traditional culture media are: BOLTON, PRESTON, SKIRROW, Mccda, KARMALI.
Typical colonies of these media can be recultivated in chromogenic (commercial) media or subjected to microscopic examination where spiral shape and mobility can be seen.
Also note that the HIPPURATE hydrolysis test is only positive for C.jejuni.
Finally, fairly accurate PCR techniques can detect living DNA (reverse transcriptase).
In old cultures or stressful situations, it takes on a non-cultivable cocoid form, which allows it to survive in food or other habitats without multiplying.
MICROORGANISM ECOLOGY
- Very sensitive to drying (airing)
- Heat, 60 ° C is enough to inactivate it
- Solar radiation
- Sodium chloride
- Freezing, -15 ° C is lethal
- PH acids <5 or basic> 9
- Microaerophilic 5% O2, 10% CO2 and with a growth at 42 ° C
In birds, C.jejuni is the most widespread species. For pigs, it’s C. coli and in cattle C. fetus. Additionally, we cam also detect Campylobacter spp. in water bodies near the farms.
Keep up to date with our newsletters
Receive the magazine for free in digital version
REGISTRATION
ACCESS
YOUR ACCOUNT
LOGIN
Lost your password?