Content available at: Español (Spanish)
The chicken’s reproductive system has four components:
- Hypothalamus
Responsible for directing hormonal operations, assisted by the adenohypophysis.
- Ovary
Initial motor of the formation of the egg – since the follicles that will transform to yolks develop there – requires the constant supply of fatty acids from the liver
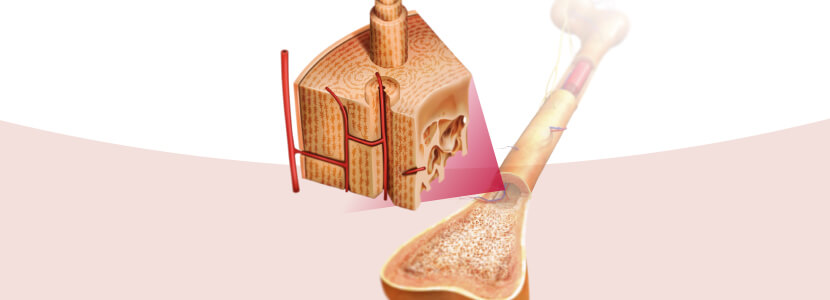
- Oviduct & Medullary bone
The shell formation requires a great partner: the medullary bone. If the cells of the uterus in charge of mineralizing the shell get minerals from the cortical bone, the bird is losing the fight in the game of bone formation: osteoblasts versus osteoclasts.
It is important to plan wisely:
- The activities to be carried out
- Management and nutrition practices to guarantee the development, growth and maintenance of the hen’s bones, especially if more than 380 eggs are desired; or to reach one hundred weeks in a production cycle without molting.
Van Sickle, more than 30 years ago, described the important aspects to keep in mind from the first day of a chick’s age until the adult hen is removed:
- Growth: relative rates with other organs and with respect to bone components.
- Development of structural and functional components of bone: related to endochondrial and intramembrane growth.
- Control of bone growth
The first two points of this proposal are not simple to carry out on a commercial farm since they are related to research centers.
However, what can be done is to construct a standard bone growth and development curve to assess the bone behavior of the birds. This is an additional variable to those who normally use metrics such as body weight, consumption, etc.
Importance of bone measurement
The importance of bone measurement is to indicate:
Table 1 details the effect of three measurements on the femur and its correlation with two variables in the egg, production and body weight.
- Specific gravity
- Egg weight
- Production
The medullary area presents a direct and highly significant relationship on the specific gravity and weight of the egg.
More area means more space for calcium fixation in the medullary bone, and from there the bird will mobilize it to mineralize the shell.
To achieve a positive effect on the variables of the egg, the work is carried out in the second stage of growth and development of the bird: weeks 14 to 24.
More area means negative affectation of these three variables.
There is important activity to implement during the first 13 weeks of life where the cortical bone develops. As expected, it directly favors – but not significantly – body weight; fundamental concept for the pre-lay stage, since it talks about the relationship between skeletal development and body weight gain.
Table 2 lists different concepts about the three stages of bone development; which leads to goals during each of them related to bone growth and development.
Stage 1: Cortical development
For the cortical bone and the supporting structure of the bird.
Stage 2: Medullary development
For the medullary bone and the construction of the nutrient reserve – especially calcium – for shell mineralization.
Stage 3: Bone maintenance
To delay the appearance of bone deterioration symptoms such as shell weakness and breakage, prolapse and cage fatigue.
Whitehead reported that chicken bone begins to weaken from the time 200 eggs are produced, corresponding to 50-52 weeks of age.
Getting the bone of the birds from a commercial farm to support the formation of the shells is challenging, because the skeleton of the modern hen is smaller than the one that was in sheds when Van Sickle proposed the 3 aspects to consider in bone development. An initial proposal is to go back to bone length measurements and construct the standard curve on each farm. The work plan presents many variations due to the different ways of producing eggs:
- Genetics –white or brown egg–
- Accommodation in the rearing and raising stage –floor or cage– and in the production stage –floor, traditional cage, automatic cage–
- Implementation of forced sexual maturity programs – darkening, black-out during release –
- Feed grain size
- Facilities for calcium carbonate supplementation in grit
Darkened Pre-lay phase
An example to highlight the importance of each of the variations proposed is in the darkened pre-lay phase. Bone problems likely began when that management technique was emulated from broiler breeders to commercial brown layers. Nothing is uni-factorial or uni-variable. Situations appeared like:
- Less skeleton in birds
- More productivity
- Better conversion
- Ambient change – although it sounds risky –
- Poultry companies that started with the darkening had strong prolapse and cage fatigue problems from week 25, and learned about the importance of the development of the medullary bone, a subject that in those days had little significance.
None of the three stages of bone development is more important than another; If one of them fails, we will have more technical work during the other two. In case of not reaching the development of the cortical bone, the following symptoms may arise:
- Birds with low body weight
- Small birds
- Apperance of a short gastrointestinal tract –medium level of probability–
- Calcium content in feed according to each physiological stage.
- Use of thick calcium carbonate – above 3mm– in feed from the sixth week of age.
- Coarse grain size of the feed from the same week.
- Reinforcement with sources of organic calcium at the time of pre-lay and start of production – stage 2 -.
- Good judgment in the use of phytases.
- Establishment of a light program: intensity and length to favor the development of the hypothalamus.
- Proportion of coarse carbonate vs. powder in production foods.
- Coarse limestone supplementation program (3 – 5 mm) in production
The difference between points 2 and 7 is related to the effect of coarse calcium carbonate on the bird; in chicks, the aim is to stimulate the growth and development of the gastrointestinal tract (it is not a direct nutritional function). In chickens it is a source of calcium with nocturnal absorption for making the shell.