Content available at: Indonesia (Indonesian) Melayu (Malay) ไทย (Thai) Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese) Philipino
Effects of Chronic Stress and Intestinal Inflammation on Commercial Poultry Health and Performance: Part II
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION: MODELS AND BIOMARKERS
There is a delicate balance between pro-oxidant and antioxidant production during homeostasis, but chronic inflammation promotes an overabundance of ROS molecules, which can be severely damaging.
- Extracellular pathogens that are too large for phagocytosis are targeted by ROS (Griffiths, 2005).
- When stimulated, RNS target intracellular/phagocytosed pathogens, extracellular pathogens, and tumor cells.
- Macrophages, the primary producers of ROS and RNS, detect and activate to eliminate bacterial infection via LPS recognition, a necessary and beneficial host mechanism (Lauridsen, 2019).
- However, prolonged exposure to high doses of LPS triggers inflammatory mediators (cytokine cascade), causing oxidative stress (Figure 2 & Figure 3).
- Nevertheless, it is essential to recognize that all forms of chronic stress (biological, nutritional, physical, chemical, or psychological) induce prolonged inflammation (Khansari et al., 2009).

In the GIT, chronic inflammation affects the integrity of the intestinal barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins leading to increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”) (Fasano, 2020), causing bacterial translocation and systemic inflammation (Ilan, 2012).
Researchers may use enteric inflammation models in a laboratory setting to examine alternative growth promoters and dietary supplements for poultry. Several intestinal inflammatory models have been developed, including:
- High NSP diets
- Dexamethasone
- Dextran sodium sulfate
- Feed restriction/ fasting
- Heat stress
Gut integrity relies on its barrier function, which can be compromised by various stressors such as oxidative stress, certain components in soy, indigestible proteins, heat stress, and infections like histomonosis.
- The removal of antimicrobial growth boosters has led to new multifactorial diseases in broilers, causing significant health and performance issues.
Dysbacteriosis, characterized by an imbalanced gut microbiota, leads to issues like reduced nutrient absorption, inflammation, and leaky gut, negatively impacting gut health.
- Poor gut health is linked to conditions such as bacterial chondronecrosis, osteomyelitis lesions, and lameness in broiler chickens.
- The gut barrier plays a crucial role in maintaining health by defending against environmental antigens.
- Its first layer consists of mucus, bacteria, IgA, and mucin, while the second layer is formed by intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) that separate the intestinal lumen from deeper tissues.
- These cells aid in nutrient absorption, tissue repair, and regulate barrier permeability through tight junctions, preventing bacteria and antigens from crossing into the body.
- As the primary contact point with the external environment, IECs serve as the host’s frontline defense.
Despite not being of hematopoietic origin, intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) play a vital role in innate immunity within the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT).
- They recognize pathogens through immune receptors, release antimicrobial molecules, and secrete hormones, neurotransmitters, enzymes, cytokines, and chemokines that link innate and adaptive immune responses.
- Damage to IECs can compromise the gut barrier, disrupt mucosal immune balance, and lead to chronic intestinal and systemic inflammation.
Research has shown that inflammatory mediators such as hormones, free radicals, enzymes, and pro-inflammatory cytokines—triggered by infections, diet, or stress—can disrupt the protein networks connecting epithelial cells.
- Additional factors like feeding oxidized fats in poultry and swine increase intestinal cell turnover and apoptosis, while mineral nutrition also impacts gut barrier integrity.
- Metals, like pro-oxidants, may cause oxidative stress and damage the barrier.
- Zinc, however, plays a key role in tight junction formation, and its deficiency has been linked to impaired barrier function.
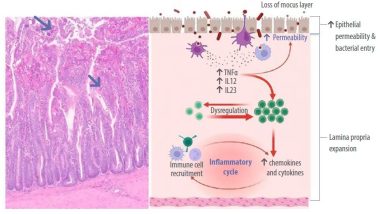
The proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is essential for animal health, welfare, and performance.
- Gut health involves factors like oxidative stress, genetics, diet, the gut barrier, and the interactions between the brain, gut microbiota, and immune system, all interconnected through complex mechanisms.
- Identifying key aspects of GIT functionality helps researchers develop biomarkers to evaluate intestinal performance in poultry.
- Due to the complexity of the GIT, multiple biomarkers are often required.
- Research on “biomarkers for intestinal integrity in poultry” has identified numerous studies, highlighting the need for effective models to induce gut inflammation and assess the effects of nutraceuticals as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters.
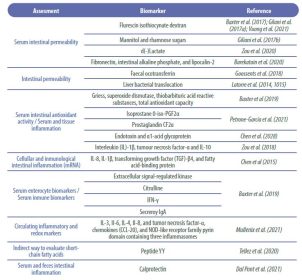
- Table 1 summarizes some related and reliable biomarkers to evaluate intestinal integrity in chickens.
DAMAGES IN POULTRY FARMING
Hans Selye’s 1975 article, “Confusion and Controversy in the Stress Field,” highlights challenges in stress research, including unclear definitions and inconsistent terminology.
Selye defines stress as “the body’s nonspecific response to any demand” and discusses the concept of “eustress” or positive stress, which some believe enhances performance and well-being.
- He argues that all stress can be harmful if not managed, emphasizing the importance of finding an optimal, tolerable stress level.
- Selye advocates interdisciplinary research, integrating psychology, physiology, and endocrinology, and encourages viewing stress as a holistic phenomenon that encompasses both biological and psychological dimensions.
Stress in humans is described as a disruption of homeostasis, which can manifest as both systemic and local stress. A specific stressor may trigger local stress, but exceeding a certain threshold typically activates the HPA axis, leading to a systemic stress response.
- Stress is classified into three types: stress (inadequate stress), eustress (good stress), and distress (poor stress).
- While stress and distress can impair physiological functions and cause pathology, eustress may promote health by optimizing equilibrium.
- Maintaining an adequate stress level is crucial for biological resilience.
- Despite the known link between stress and chronic diseases, few physicians understand how dysfunction in the stress management system (HPA axis) alters pathophysiology.
- Research has provided valuable insights, but the clinical impact of stress on chronic disease management remains a significant challenge.
Chronic neuroendocrine-immune interactions in poultry can lead to infections, reduced feed intake, impaired feed conversion, and carcass condemnation.
- Heat stress is a major ecological stressor in chicken farming, affecting performance, immunity, and food safety.
- It triggers changes in proteins, lipids, and metabolic rates, with heat shock proteins produced as a defense.
- The hypothalamus and HPA axis play key roles in maintaining homeostasis by releasing steroid hormones and regulating stress responses.
- The activation of glucocorticoids helps liver gluconeogenesis and boosts epinephrine production, supporting the animal’s adaptation to stress.
Flock density, or the number of chickens in a given space, can increase social stress among birds, as higher density leads to more competition for resources like food, water, and space.
- This stress can reduce immune function, making chickens more susceptible to diseases like enteritis, and can also lead to behaviors such as feather pecking and cannibalism, which create entry points for infections.
- High density can also worsen heat stress, which negatively impacts feed intake, egg production, and increases mortality.
Managing flock density carefully, including providing adequate space and resources, is essential to reduce social stress and improve chicken health. Additionally, factors like breeder age, chick gender, and breed are related to chick mortality, and stress during transport to processing plants requires attention.
Inflammation is the final stage of the stress response, triggered by cellular harm, and is regulated by immune and endocrine mechanisms.
- Stress activates the autonomic nervous system and hormones like adrenaline and glucocorticoids, preparing the body for “fight-or-flight.”
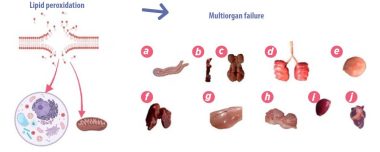
- While this response is meant to be short and acute, prolonged stress keeps stress hormones and pro-inflammatory molecules circulating, leading to oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and damage to cells and mitochondrial membranes.
The cell and mitochondrial membranes, composed of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and transport channels, regulate cell functions like adhesion, ion conductivity, and signaling.
- Prokaryotes, the simplest organisms, have provided insights into the cell membrane’s extraordinary properties, acting as both a protective barrier and the “brain” of the cell.
- Prokaryotes, including bacteria, use their membranes for nutrient acquisition, communication, and information processing, much like a neurological system.
- Any damage to the membrane can severely affect the cell’s function, whether in prokaryotes or eukaryotes.
According to the endosymbiotic theory, essential eukaryotic organelles evolved from symbiotic relationships between prokaryotes. Around two billion years ago, a free-living bacterium was incorporated into a host cell, forming a symbiotic relationship.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are believed to have evolved from proteobacteria and cyanobacteria, respectively, through symbiotic relationships that significantly impacted evolution.
- Mitochondria, known as the “powerhouse of eukaryotic cells,” are crucial for energy production, signal transduction, and apoptosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction is linked to various diseases in animals and plants.
- Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, caused by reactive oxygen species, disrupt cell and mitochondrial membranes, affecting cell function. This phenomenon, recognized as a major health risk in humans, also applies to poultry.
The balance of microbiomes on mucosal surfaces is crucial for biological and physiological processes.
- Dysbiosis, or the imbalance of microbiota in the GIT, leads to intestinal inflammation and compromised intestinal integrity.
- The composition of feed and the viscosity of intestinal contents affect microbial development, particularly in the small intestine.
- High non-starch polysaccharide diets in monogastric animals require exogenous enzymes to prevent negative effects like intestinal irritation and decreased performance.
- Studies in chickens and turkeys have shown that rye increases digesta viscosity, bacterial translocation, and microbiota changes, impacting bone mineralization.
- The nutritional value of grains influences energy use in chicken diets.
Low-grade intestinal damage and inflammation reduce feed efficiency, which is costly for the poultry industry. Both endogenous and exogenous factors, including biological, nutritional, environmental, and chemical stressors, can disrupt the GIT’s balance, leading to inflammation, dysbacteriosis, and impaired nutrient absorption. Chronic stress further exacerbates these issues.
Determining the optimal microbiome for chickens involves several steps:
- Reviewing existing literature on beneficial microbes.
- Analyzing fecal or intestinal samples to establish a healthy microbiome benchmark.
- Conducting experimental trials with different diets or supplements.
- Using metagenomic sequencing for a detailed understanding of microbial diversity.
- Analyzing data to identify patterns linking the microbiome to chicken health and productivity. This ongoing research aims to enhance poultry health and performance.
Intestinal homeostasis refers to a balanced state without inflammation or excessive secretions.
- While physiological inflammation helps maintain tolerance to dietary antigens and gut microbiota, chronic inflammation can lead to excessive fluid secretion and nutrient diversion to the immune response.
- This process can impair growth, cause muscle catabolism, and reduce body weight gain.
- Damage to the intestinal barrier further reduces nutrient absorption and increases permeability.
- Factors like high NSP diets without added enzymes can cause dysbiosis and inflammation, negatively affecting poultry performance.
In poultry, increased water excretion can be due to physiological diuresis or diarrhea, often linked to nutritional issues that affect water recovery or cause enteritis.
- Watery excreta may also result from digestive secretions, osmotic effects of the diet, or electrolyte imbalances.
- Inflammation in the renal or gastrointestinal lining hampers water and nutrient transfer, leading to more water, mucus, and undigested nutrients in the excreta.
- This worsens litter quality and can be exacerbated by infections or toxins.
Enteric inflammation in poultry, caused by heat stress, enteropathogens, or nutritional disturbances, leads to undigested feed, increased intestinal permeability, and reduced feed efficiency.
- This chronic inflammation, linked to conditions like coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis, results in significant economic losses for the poultry industry.
Nutraceuticals with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-modulating properties may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in poultry by improving gut health.
COUNTERMEASURES
- To prevent intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress in poultry, a multifactorial approach is needed.
- Strategies include using probiotics, prebiotics, phytogenic substances, essential oils, and trace minerals.
- These helps improve nutrient utilization, reduce pathogen colonization, and modulate the intestinal microflora, potentially alleviating the negative effects of chronic inflammation and oxidative stress on the gastrointestinal system.
OUTLOOK
The study of the complex relationship between microflora, diet, environment, genetic factors, and diet components in production animals, especially production birds, is a key area of nutrition with significant future impact on global food production.