General principles of bacterins
Content available at:
Español (Spanish) Português (Portuguese (Brazil))
This article is a practical guide to induce optimal levels of immunity and minimize the risk of adverse effects associated with the use of bacterins in broiler breeders.
A good vaccination program, combined with appropriate management and good biosecurity, plays a key role in promoting the health, well-being and productivity of broiler breeders.
Inactivated bacterins or bacterial vaccines can be a valuable tool in breeding programs, to stimulate high levels of immunity against pathogens such as:
General principles of bacterins
Age of Administration
Due to the potential of bacterins to cause a strong reaction, they are generally administered between 8 and 10 weeks of age when broiler breeders have enough weight and muscle mass to assimilate them. A second dose is recommended between 18 and 20 weeks so that the flocks can overcome the reaction without compromising their weight, uniformity, sexual development and start of egg production.
It is recommended to remove the bacterial from the refrigerator around 24 hours before administration to temper them. 
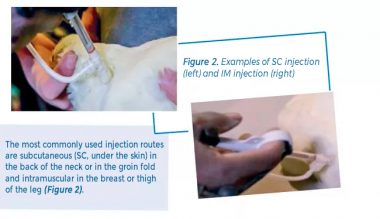

The success of the bacterins and the severity of the reaction depends on the following factors:
In general, when the bacterins are applied correctly through the subcutaneous route (SC), there is less reaction when compared to intramuscular injection (IM). 
SC injections
It is essential to use new sterile needles and replace them periodically (at least once every 500 birds). For SC injections, it is recommended to use 18-19 gauge needles and 10 to 12 mm (0.4 to 0.5 in.) Long. For IM injections, 18-gauge and 0.25-inch long needles are recommended. Blunt neeedles or with damaged bevels should be replaced immediately so as not to cause damage to the birds’ tissues.
IM injections
When the IM route is used, the breast muscle is the best possible site as its thickness offers good injection cushioning. When injecting into the breast, make sure that the needle is located 2.5-3.8 cm (1-1.5 in.) Away from the sternum or keel bone (Figure 5) and place the needle in the upper third of the breast, downwards at a 45 ° angle, preventing the application of the vaccine within the abdominal cavity. The application of bacterins to the leg muscles is not common in broiler breeders and in general should be avoided to prevent adverse reactions. 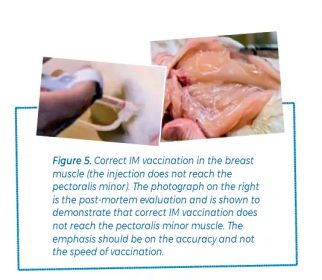
Verification Methods
Inspection of the location is recommended within one hour after vaccination. Wet feathers indicate that the vaccine was misapplied. To visually evaluate the procedure after intramuscular (IM) application, it is suggested to cull some birds that are sexing errors (using a suitable method) and inspect the injection site. 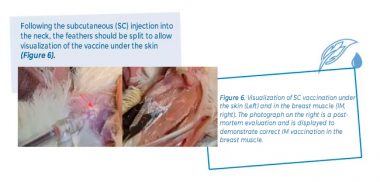
Bacterial Responses & Reactions
If the birds are depressed and lethargic for a few days due to the reaction, it is recommended to adjust the amount of feed to stimulate and give the flock an additional amount of energy. This helps maintain weight uniformity and helps birds to cope with both tissue and systemic reaction. The post-bacterial hemorrhagic syndrome that occurs in some cases is an adverse reaction that is possibly due to the presence of endotoxins in some bacterins. 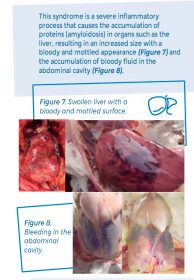
Scars at the injection site followed by application to the breast can result in seizure problems when the birds are processed at the end of the production cycle. These scars tend to be more visible when oil emulsified bacterins are used compared to inactivated viral vaccines. 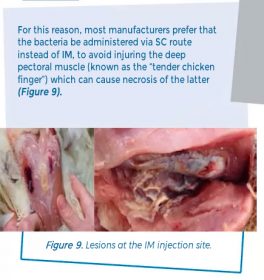
Subscribe now to the poultry technical magazine
AUTHORS

Layer Longevity Starts at Rearing
H&N Technical Team
The Strategy for a Proper Infectious Bronchitis Control
Ceva Technical Team
Elevate Hatchery Performance with Petersime’s New Data-Driven Incubation Support Service
Petersime Technical Team
Maize and Soybean Meal Demand and Supply Situation in Indian Poultry Industry
Ricky Thaper
Production of Formed Injected Smoked Chicken Ham
Leonardo Ortiz Escoto
Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Food Chain and Novel Strategies of Bacterial Control
Edgar O. Oviedo-Rondón
GREG TYLER INTERVIEW
Greg Tyler
Insights from the Inaugural US-RSPE Framework Report
Elena Myhre
Newcastle Disease: Knowing the Virus Better to Make the Best Control Decisions. Part II
Eliana Icochea D’Arrigo
Avian Pathogenic E. coli (APEC): Serotypes and Virulence
Cecilia Rosario Cortés
The Importance of Staff Training on Animal Welfare Issues in Poultry Industry
M. Verónica Jiménez Grez
Rodent Control is a Key Factor in Poultry Biosecurity and Sustainability
Edgar O. Oviedo-Rondón