Content available at: Indonesia (Indonesian) Melayu (Malay) ไทย (Thai) Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese) Philipino
Soybean in Poultry
The global population is increasing day by day, which results in a significant increment for global demand of food and feed (Parrini et al., 2023).
By 2050, it is estimated that the world population will be more than 9 billion people; subsequently agricultural production is expected to show an increment by 50% (Lombardi et al., 2021).
In poultry nutrition, protein feeds are one of the most expensive and limiting ingredient in diet formulations (Parisi et al., 2020) and one of the most important protein sources for poultry is soybean.
For this reason, the need for soybean is increasing day by day and soybean production is becoming more and more important especially in animal nutrition with a usage amount as 67% of the animal feed market (Pettigrew et al., 2002).
Soybean Production Statistics
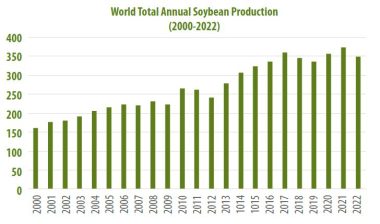
As seen in Figure 1, soybean production in the world constitutes an increasing graph. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture data, 398.210 million metric tons of soybeans were produced worldwide in 2023. As a result of increasing demands, soybean production is expected to increase even more every year. The majority of these high production capacities in soybean production are in 3 countries that are active in production.
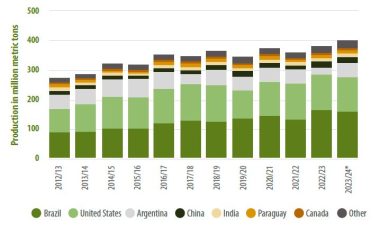
As can be seen more clearly in Figure 2, the United States and Brazil account for more than half of total soybean production. The 3rd largest producer is Argentina, followed by China. Other countries account for a much smaller share of total production. The largest producers, Brazil, the United States and Argentina, account for about 70% of total production.
Soybean Nutrient Content and Use in Poultry Feeding
Soybean (Glycine max L.) is a high quality protein source due to its favorable attributes such as relatively high protein content and suitable amino acid profile except methionine, minimal variation in nutrient content, ready availability year-round, and relative freedom from intractable antinutritive factors if properly processed.
The most important quality criteria’s for soybean are crude protein, moisture, KOH and crude oil contents.
These criteria vary greatly depending on the origin of the soybean.
- In addition to these analyses, physical analyses such as seed size, color and seed shape are also important in soybeans.
- It has been reported that geographical location of soybean production, soybean variety, and processing methods affects the crude protein and amino acid composition of soybean meal (Parsons et al., 1991, 2000; de Coca-Sinova, 2008, 2010; Baker et al., 2011).
In poultry nutrition, soybeans cannot be used directly in feed formulation due to its high oil content, cellulose in the hull and anti-nutritional factors.
- To avoid the negative effects of cellulose, soybeans are dehulled.
They are then cooked, which greatly reduces the anti-nutritional actors, and then the oil is separated to produce soybean meal.
Therefore, the by-products of soybean as soybean meal and soybean oil is used in poultry nutrition, with an average value of 30% of diet.
Soybean is a rich source of vegetable protein in terms of the variety and amount of amino acids it contains.
- One of the features that makes soybeans stand out from other vegetable proteins in poultry nutrition is its high lysine content.
- However, if soybeans are exposed to more heat than necessary in the heating applied to destroy the anti-nutritional factors in soybeans, some essential amino acids, especially lysine and arginine, are either destroyed or rendered unusable.
Changes in Nutrient Content of Soybean Grown in Different Countries
The aim of this article was to determine the variation of crude protein and crude fat values of soybeans according to origin and to observe the differences in nutritional value between producing countries.
A total of 227 soybean samples from six countries of origin (Ukraine, Argentina, Brazil, USA, Paraguay and Uruguay) were analyzed for crude protein and crude oil content.
- The crude protein and crude fat content of the soybeans samples was determined according to AACC Method (46-11.02, 30-25.01, International, 2010a, 2010b).
- The obtained data were analyzed using the GLM procedures of statistical software (Minitab, 2013). Significant differences among the means were compared using the Tukey test and were considered statistically different at a level of P <0.05.
The crude protein content of soybean samples from 6 countries of origin (Ukraine, Argentina, Brazil, USA, Paraguay and Uruguay) varied between 30.7% and 38.8% when compared by country of origin. The lowest average crude protein content was observed in Ukraine origin soybeans with 33.9%, while the highest crude protein content was observed in USA origin soybeans with 35.6%.
- The crude oil content of soybean samples from 6 countries of origin varied between 17.7% and 23.0% when compared by country of origin. The highest and lowest crude oil contents were observed in soybeans produced in Paraguay (21.3%) and USA (19.2%, P<0.005).
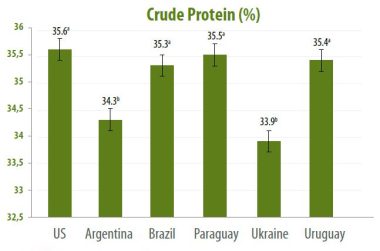
Crude protein content of soybeans grown in different countries is shown in Figure 3. As shown in the figure, crude protein content was lower in soybeans originating from Argentina (34.3%) and Ukraine (33.9%) compared to other countries (P<0.001).
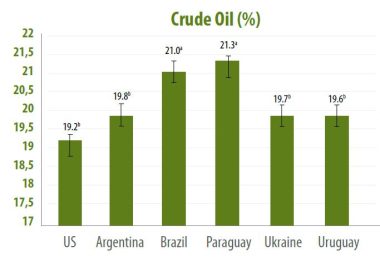

Crude oil content of soybeans grown in different countries is shown in Figure 4. As shown in the figure, the highest average oil content was observed in soybeans produced by Brazil (21.0%) and Paraguay (21.3%) (P<0.001).
- The soybean meal is a primary source of protein in diets; therefore, any factors affecting the protein content of soybean could have major interest for feed industry.
- On the other hand, fat content of soybean has also crucial importance to the industry because of its high economic value.
- It is well known that the soybeans grown in different environmental conditions and agricultural practices cause huge variations in quality parameters.
- Besides, the meal processing conditions, e.g. processing temperature, moisture and drying time, cause differences in both chemical composition and quality of soybean meal (Thakur and Hurburgh, 2007).
- According to Zhang et al. (2024), soybeans with a moisture content of less than 13% and a crude fat content of more than 20% are accepted as high-oil soybeans.
- In a previous study performed by Grieshop and Fahey (2001), soybeans from China had a higher crude protein (42.1%) and a lower fat content (17.3%) than those from Brazil (40.9% and 18.7%) and US (41.6% and 18.7%) on a dry matter basis.
- Grieshop and Fahey (2001) reported that the fat content of soybeans from both Brazil (range between 18.0 and 19.8%) and the U.S. (17.89-19.65%) were quite stable, however fat content of soybeans from China showed many variations from 14.5% to 18.0%.


Although the high nutritional value of soybean as a plant protein source provides an efficient usage in poultry nutrition, both the social and environmental impact of the soybean industry and genetically modified soybean production has led to a growth in demand for more sustainable alternative protein sources (Gkarane et al., 2020).
The production and supply of soybean are critical steps due to their environmental impact and feed/ food competition for land use.
- Therefore, research is focusing on finding alternatives to replace soybean partially or totally.
- However, alternative ingredients should ensure similar growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality characteristics compared to conventional soybean-based diets (Silvia Parrini et al., 2023).

- Among the most innovative feeds, microalgae have been gaining attention in the last few years thanks to their high protein content and the potential to cultivate them without using arable land.

Conclusion
Crude oil and crude protein analyses of 227 samples collected from 6 different countries show that;
- As environmental conditions change in soybeans, large differences in nutritional values can occur.
- Differences in nutritional value represent high economic values for the feed industry.
- However, in some cases, despite the good nutritional value of soybeans, problems such as low crude protein, high levels of urease or low protein digestibility are encountered in the meal produced due to improper processing practices.
- These criteria are of great importance for poultry nutrition.