Content available at: Indonesia (Indonesian) Melayu (Malay) ไทย (Thai) Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese) Philipino
The development of poultry and swine farming systems with characteristics of intensive production has been supported by establishing a circuit that entails the production of balanced feed on a large scale.
In turn, balanced feeds have been structured based on the use of corn as the main energy component of the feed, with very particular advantages over other cereals, such as the fact that they do not have anti-nutritional compounds within their components.
However, since the 1970s, other cereals have been included in the formulation of commercial diets for poultry and pigs.
- In South America, particularly in Venezuela, after corn, grain sorghum is the other cereal used by the balanced feed industry.
- Most of these sorghums contain condensed tannins (CT) within their components, which have been linked in non-ruminants with an adverse effect on digestion and the metabolism of nutrients.
This report highlights relevant concepts related to the toxicology of genotypically brown sorghums (GBS), emphasizing aspects related to their intrinsic and extrinsic toxicities.

TOXICOLOGY OF GENOTYPICALLY BROWN GRAIN SORGHUMS
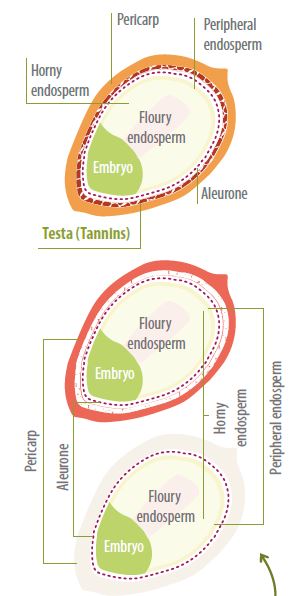
The GBS designation is given by the presence of a defined layer of cells called the testa (Rooney and Miller, 1981; Rumbos, 1986). This layer is present and highly pigmented in the initial grain formation stage.
- As a highly significant structural characteristic, it has been determined that GBSs with a highly developed and highly pigmented testa have high total polyphenol and CT contents compared to those with little or no development of this layer (Doherty et al., 1987; Ciccola, 1989).
- This fact suggests that it is in this layer where the cells that produce these compounds are located. Therefore, those cultivars that do not have a testa (genotypically white sorghums) do not contain CT; their nutritional value is around 96-98% in relationship with corn (Sullivan, 1987).
Intrinsic Toxicity: Polyphenolic Compounds
From a chemical point of view, polyphenolic compounds can be classified into three groups:
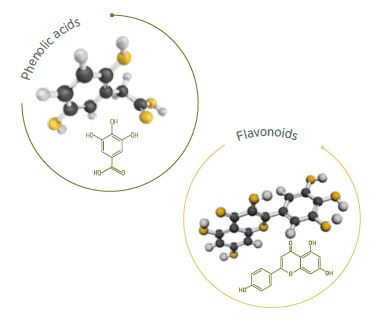
Phenolic acids are found in all sorghum cultivars and the vast majority of flavonoid compounds, while tannins, particularly condensed ones, are present only in GBS, possessing a pigmented testa, resistant to bird attack and enzymatic degradation (Hahn et al., 1984).
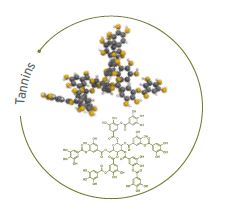
Tannins
Tannins are a complex of phenolic polymers that constitute some of the most numerous and widely distributed natural products in many vegetables, including trees, fruits, and grasses.
Their presence in cereals is rare, and in the case of sorghum, they are only found in genotypically brown cultivars (Mehansho et al., 1987a).

Hydrolyzable Tannins
Research by Hahn et al. (1984) made it possible to distinguish two large groups:
Its main representative is tannic acid, which unfolds into its characteristic components: a sugar and a phenolic acid (gallic acid or ellagic acid) when subjected to treatment with acid or alkaline solutions or with hydrolytic enzymes such as tannase.
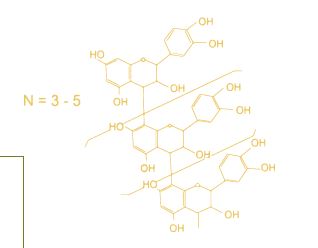
Condensed Tannins
They are high molecular weight (500 to 3000 daltons) phenolic polymers, soluble in water, which result from the condensation of flavan-3-ols or catechin units and are referred to as proanthocyanidins (Salunkhe et al., 1982).
- CTs have the ability to precipitate alkaloids, gelatins and other proteins, forming stable tannin-protein complexes; which will lead to protein inactivation with subsequent protein precipitation (Aw y Swanson, 1985).
- This type of tannin has been scientifically associated with the deterioration of the nutritional value of GBS and the productive response in poultry (Hahn et al., 1984; Jaramillo, 1992).
Extrinsic Toxicity: Mycobiota Metabolites
The presence of molds as natural contaminants of plant inputs, particularly grain sorghums, is significant since, in addition to the intrinsic toxicity of the grain generated by the presence of CT, a new toxic component is incorporated.
- This new toxic component is extrinsic in nature. It is represented by natural contamination by mycotoxins when those molds have the genetic capacity to produce one or more of these chemical compounds.
Once generated in sorghum grains, mycotoxins can be ingested through feed, causing organic dysfunctions in birds that negatively compromise overall health and production rates.

In production animals, particularly poultry and pigs, the effects that could be generated by the consumption of GBS high in CT and contaminated with mycotoxins are unknown since research efforts in this type of sorghum have focused on the study of the antinutritional effects of tannins.

TOXICOLOGY OF THE TRINOMIAL CAUSE – EFFECT – RESPONSE
The trinomial CAUSE – EFFECT – RESPONSE can be defined as the action of causal agent on biological systems, giving rise to an effect that is expressed through a response or measurable and/or visible manifestations (Jaramillo, 2005).
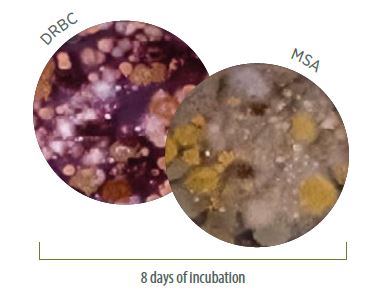
Photo 1. Mycobiota in sorghum. Petri dishes in DRBC and MSA media at eight days of incubation. Source: Dr. Marta Jaramillo (1999 – 2018)
Currently, it is known that in the GBS:
- The CAUSE component is represented by the intrinsic presence of CT and by the extrinsic presence of metabolites produced by a mycobiota that contaminates the grain internally and externally in the field and to which an external mycobiota load is added during storage and transport.
- The EFFECT component is represented by the generation of effects developed by the CAUSE component in organs and tissues of the different biological systems.
- The RESPONSE component is linked to the manifestations exhibited by the animals as a consequence of the EFFECT component; These can be measured quantitatively (Jaramillo, 2005).
CONDENSED TANNINS
Metabolic Toxicity
Direct absorption of CTs does not seem to be possible. Perhaps, due to the anatomical barriers encountered and, more specifically, due to the large size of the tannin polymers, which are not degraded to their final products by the gastrointestinal tract enzymes.
However, some evidence of metabolic toxicity has been related to a possible action of CT and other chemical compounds present in the sorghum grain, such as:
- The studies by Sell and Rogler (1983) show possible metabolic toxicity of CT by finding an increase in the activity of the enzyme UDP-glucuronyltransferase in birds that consumed sorghum high in tannins in relation to those fed with sorghum low in tannins.
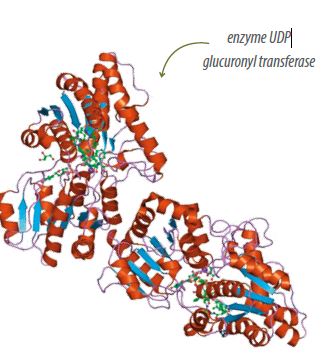
This enzyme is known to be involved in the detoxification processes of phenolic compounds. On this basis, an increase in its activity could imply the absorption of CTs through the intestinal wall.
- This hypothesis is reinforced by the observations of Martin-Tanguy et al. (1976), who report that tannins reduce the metabolic use of amino acids.

- These findings would indicate the presence of an injurious agent that could be related to the action of these compounds or to that of flavonoid oligomers.
MYCOBIOTA METABOLITES
The research of Jaramillo and Wyatt (2000ab, 2001ab, 2002ab, 2003ab, 2004ab) were conducted as pioneers in the study of the trinomial of toxigenicity in grain sorghums, highlighting that the elements of said trinomial would be represented by:
- Condensed Tannin Content (CTC).
- Mycobiota Contamination (MC).
- Toxigenic Potential of the Mycobiota (TPM).
This trinomial has left open an exciting area of investigation.
- In their different studies, Jaramillo and Wyatt discuss significant findings that currently allow us to understand the toxigenicity of GBS under a new concept of an integral system of Condensed Tannins – Mycobiota Metabolites, where its development dynamics are highlighted.
- This toxigenicity system occurs naturally under field conditions given the per se presence of tannins in the grain and its internal and external contamination by mycobiota.

CONCLUSION
In the study of the toxicity of GBS, a new approach concept that involves the trinomial: CTC – MC – TPM allows for a more accurate and representative comprehensive evaluation of the toxicity per se of the grains, of the contamination events that occur both at the field and storage level and the effects on birds and pigs where they generate an adverse response on the function of different organs and systems; being the young animals the most affected.

Understanding its toxicity will lead us to more efficient and rational animal nutrition and feeding use.

Source: Dr. Marta Jaramillo (2016)
References upon request