02 Apr 2025
The Earth’s Fever: Understanding and Addressing Global Warming
Our planet is running a fever. This isn't a metaphor; it's a stark reality. Global warming, or climate change, refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature due to the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities.
Our planet is running a fever. This isn’t a metaphor; it’s a stark reality. Global warming, or climate change, refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average temperature due to the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities. Essentially, we’re trapping more of the sun’s heat within our atmosphere.
The Impact : A Cascade of Consequences
The repercussions of this warming trend are far-reaching and devastating
- Rising Sea Levels: Melting glaciers and thermal expansion of water are causing oceans to rise, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires disrupt lives and economies.
- Disrupted Ecosystems: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are altering habitats, leading to species extinction and biodiversity loss.
- Agricultural Disruptions: Shifts in weather patterns affect crop yields, threatening food security.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased carbon dioxide absorption by oceans is making them more acidic, harming marine life, particularly coral reefs.
- Human Health Impacts: Heatwaves, air pollution, and the spread of infectious diseases are becoming more prevalent.
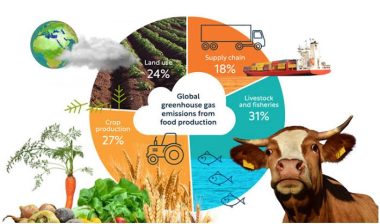
The Industrial Culprits : A Breakdown
Several industries contribute significantly to global warming
- Fossil Fuel Industry: The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy production is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Transportation: Vehicles, airplanes, and ships release substantial amounts of CO2 and other pollutants.
- Manufacturing: Industrial processes, including cement and steel production, generate significant emissions.
- Agriculture and Land Use: Deforestation, livestock farming, and the use of fertilizers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, including methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
Poultry and Dairy: The Livestock Contribution
Yes, poultry and dairy farming do contribute to global warming. Here’s how:
Continue after advertising.
- Methane Emissions: Livestock, particularly cattle, release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, through their digestive processes (enteric fermentation).
- Nitrous Oxide Emissions: Manure and fertilizer use release nitrous oxide.
- Deforestation: Expansion of pastureland and feed production often leads to deforestation, releasing stored carbon.
- Feed Production: Growing crops for animal feed requires energy and resources, contributing to emissions.

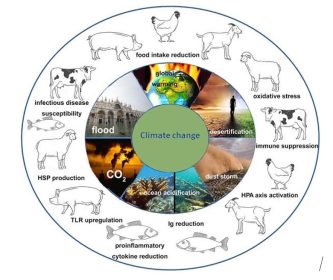
The Backfire: A Looming Threat
The very industries that contribute to global warming are also vulnerable to its effects
- Heat Stress: Extreme heat can reduce livestock productivity and increase mortality.
- Feed Availability: Droughts and floods can disrupt crop yields, impacting feed availability and prices.
- Disease Outbreaks: Climate change can create favorable conditions for disease vectors, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
- Water Scarcity: Water is essential for livestock and poultry farming, and climate change is exacerbating water scarcity in many regions.


A Global Call to Action: Mitigation and Adaptation
Preventing catastrophic climate change requires a concerted global effort
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Shifting away from fossil fuels to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources is crucial.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through improved technologies and practices.
- Sustainable Transportation: Promoting electric vehicles, public transportation, and alternative fuels.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Adopting practices that reduce emissions, such as precision agriculture, improved manure management, and reduced deforestation.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Developing technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees to absorb carbon dioxide.
Responsibilities in the Poultry and Dairy Sectors
Even as vital food security industries, poultry and dairy must embrace sustainable practices
- Improved Manure Management: Implementing technologies to reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions from manure.
- Feed Optimization: Improving feed efficiency to reduce the amount of feed required per unit of product.
- Precision Livestock Farming: Utilizing technology to optimize animal health and productivity, reducing resource use.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Utilizing solar and wind energy in farm operations.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Sourcing feed from sustainable suppliers.
Stakeholder Responsibilities
- Broiler Integration Companies and Large Egg Layer Farmers: Should invest in and implement sustainable practices, improve manure management, and optimize feed conversion ratios. They should also explore renewable energy sources for farm operations.
- Milk Procurement Dairy Companies: Should encourage and support sustainable practices among dairy farmers, invest in methane reduction technologies, and promote sustainable feed sourcing. They should also focus on efficient transportation and processing.
- Poultry and Cattle Feed Manufacturing Companies: Should focus on sustainable sourcing of ingredients, minimize waste, and explore alternative feed ingredients that reduce environmental impact.
The challenge is immense, but not insurmountable. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainability, we can mitigate the impacts of global warming and build a more resilient and sustainable future for all.
Sources: Available upon request