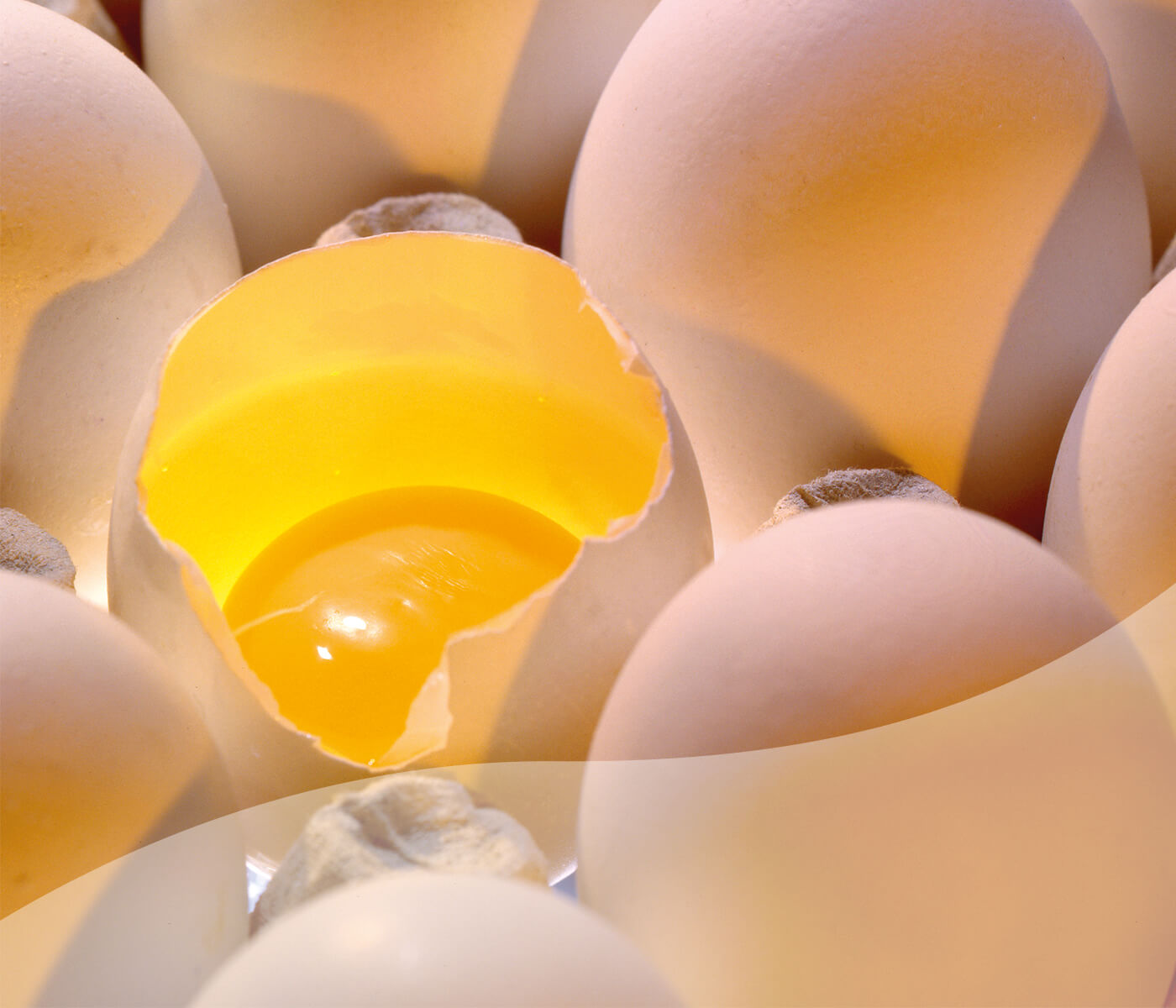
Hatching egg quality has a significant impact on hatchability and chick quality. By making egg quality control a part of the routine procedures in the hatchery, you will be able to improve your hatch results. Although it is fairly easy to evaluate external egg quality by checking the egg’s exterior, it can be more challenging to perform deeper checks on a regular basis.
A hatching egg is a protected space for the chicken embryo to develop in. Inside the egg are all the essential nutrients and mechanisms to support an optimal development and growth of the embryo. However, while the egg is formed in the reproductive tract of the hen, various events can occur that cause irregularities in eggs.

An overview of the most important interior quality factors is given below.
1. EGG FERTILITY
A first parameter is whether the egg has been fertilised or not. Hatching eggs can be analysed before incubation on arrival at the hatchery to distinguish fertile eggs from infertile eggs.
This requires a specific technique that needs to be built up by practice. When applied, however, a disadvantage of the technique is the loss of valuable hatching eggs due to the destructive procedure.



Figure 1. A fertile egg with blastoderm on the left; an infertile egg with blastodisc on the right
| It is a well-known fact that the fertility goes down as flock age increases, but a sudden drop in fertility could be an indication of a breeder problem and a reason to perform deeper analysis. |

After point of lay, the blastoderm consists of approximately 60,000 cells. Inappropriate handling and storage at the breeder farm, during transportation or at the hatchery will
Keep up to date with our newsletters
Receive the magazine for free in digital version
REGISTRATION
ACCESS
YOUR ACCOUNT
LOGIN
Lost your password?