Content available at: العربية (Arabic)
Properly ventilating poultry houses is an art in itself. And is it wise or not to ventilate on foggy days? Relative humidity and other factors play an important role to provide a good climate and growing conditions inside the house.
- There is a concern amongst many poultry producers that bringing in fresh air on a foggy morning will lead to an increased incidence of litter caking.
- This is due to belief that the foggy air entering house through side wall inlets contains a large number of small water droplets which will end up being deposited onto the surface of the litter.
- The concern is great enough that some producers will decrease minimum ventilation settings on foggy mornings in an effort to keep from bringing in this excess moisture.
- Though on the surface this practice may sound logical, though foggy air does in fact contain more moisture than non-foggy air, the difference is far less than most would believe and reducing ventilation rates on foggy mornings can in fact dramatically increase the likelihood of litter caking.
Though foggy air appears to be packed with moisture, it isn’t.
First, a droplet of fog is extremely small, roughly 10 microns in diameter (0.0004″ / 0.01 mm)1. To put this in perspective, the typical rain droplet is approximately 2,500 microns in diameter (0.1″ /2.5 mm), 250 times the size of a fog droplet (Figure 1).
- Since a fog droplet is essentially microscopic, it would take roughly 200 million fog droplets just to fill the cap from a plastic soda bottle! There are approximately ten million fog droplets in a cubic foot of air.
- Which sounds like a lot, but since they are so small, the actual amount of water they add to each cubic foot (28 liter) of air is insignificant, roughly 0.0002 ounces (0.006 ml) or 0.2 ounces (6 ml) in every 1,000 cubic feet (2.800 liter).
The moisture in the air you can’t see, is far greater than the moisture you can see on a foggy morning.
- On a cold, damp morning (40oF / 4,5 C0 @ 100% Rh) there is approximately 6 ounces (177 ml) of invisible moisture in every 1,000 cubic feet (2.800 l)of air brought into a house.
- If it is foggy outside, the amount of moisture in the air would increase to roughly 6.2 ounces (183 ml), an increase of only 3%.

Figure 1. Relative size of particles (the average fog droplet is roughly the size of a red blood cell)
The amount of moisture in foggy air appears greater than it actually is because we are unable to see through an individual droplet of fog due to light refraction.
- Up close, even though there may millions of droplets within a foot or two of your nose, they are so small that your sight will not be obstructed.
- But the farther away you look, the greater the number of droplets you are looking through, each of which is obstructing a very small portion of your view.
- Millions of small white dots turn into billions, trillions, quadrillions, quintillions, etc. as you look further and further away. Eventually, the additive effect of all the droplets will totally obstruct a person’s view.
- The denser the fog, the quicker a person’s view is obstructed. But it is important to keep in mind that even in a very dense fog there is still relatively very little additional moisture in the air.
Air direction important
In many ways, whether litter moisture increases on a cool, damp morning has more to do with where incoming air goes once it enters a house, than the moisture content of the air.
- If the incoming air quickly falls to the floor upon entering a house, it will chill the birds and remove little moisture from the litter, leading over time to caked litter…after all, it is difficult dry anything with cool, damp air.
- But, if the same air moves along the ceiling until it just makes it to the center of the house, then gently moves down toward the floor, the story is very different. We want to maximize the distance the incoming air travels before moving down to floor level so it can be thoroughly heated by the warm air collecting at the ceiling that has been put off by the heating system as well as the birds (Figure 2).
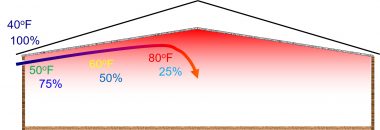
Figure 2. Ideal inlet air flow pattern to maximize the warming and drying of the incoming air
During the time the air spends near the ceiling, the temperature of the air increases and the relative humidity of the air decreases, making it easier to remove moisture from the litter without chilling the birds. In fact, for every 20o F (6,7 0 C) the temperature of the incoming air increases, the relative humidity is in cut in half due to the increased moisture-holding capacity of warm air and as a result, the ability of the air to remove moisture from the litter is dramatically increased.
Keep up to date with our newsletters
Receive the magazine for free in digital version
REGISTRATION
ACCESS
YOUR ACCOUNT
LOGIN
Lost your password?